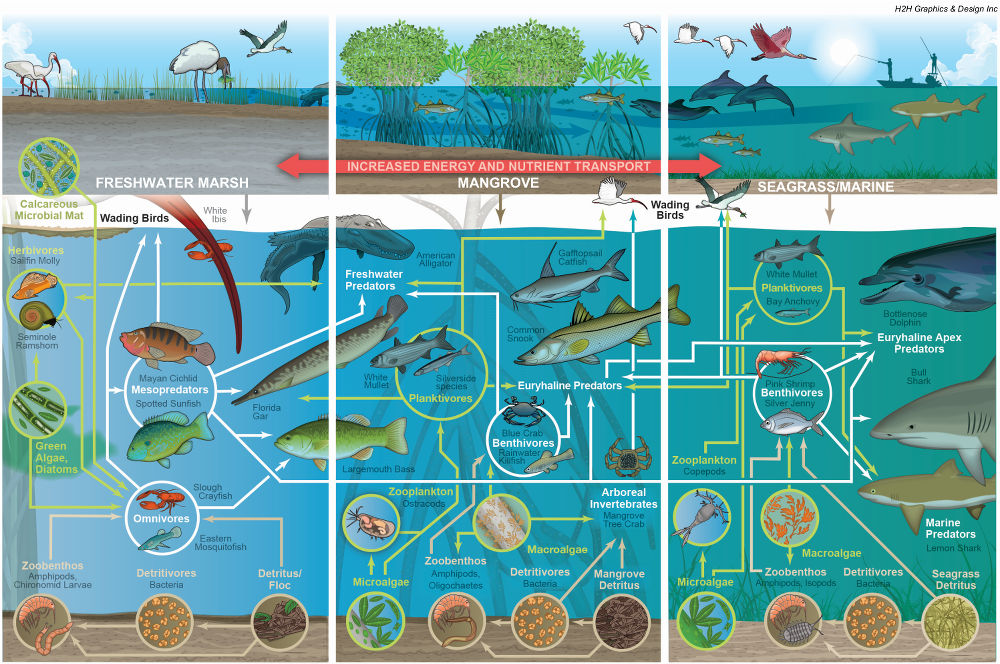
## The Everglades Food Chain: A Deep Dive into Florida’s Delicate Ecosystem
The Everglades, a vast subtropical wetland in South Florida, is a unique and complex ecosystem. Its intricate network of life depends on a delicate balance, with the **food chain Everglades** serving as the backbone of this biodiversity. Understanding this food chain is crucial for appreciating the fragility of this natural wonder and the importance of conservation efforts. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Everglades food chain, its components, its challenges, and its future. We aim to provide you with the most comprehensive and up-to-date information, drawing on expert knowledge and research to illuminate this vital ecosystem. Recent studies highlight the increasing threats to the Everglades, making understanding its food chain more important than ever.
**What You Will Gain From This Article:**
* A comprehensive understanding of the Everglades food chain and its components.
* Insights into the ecological roles of various species within the Everglades.
* Knowledge of the threats facing the Everglades food chain.
* An appreciation for the importance of conservation efforts.
* Expert perspectives on the future of this unique ecosystem.
—
## Understanding the Everglades Food Chain
The **food chain Everglades** represents the flow of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem, starting with primary producers and moving through various consumers. It’s not a simple linear pathway, but rather a complex web of interactions. The Everglades food chain differs from other ecosystems due to its unique conditions: shallow freshwater, fluctuating water levels, and a subtropical climate. These conditions create a specific set of challenges and opportunities for the organisms that live there.
### Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The food chain is built upon several key concepts:
* **Primary Producers:** These are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis. In the Everglades, the primary producers are primarily plants, algae, and phytoplankton.
* **Consumers:** Consumers are organisms that obtain energy by eating other organisms. They are categorized as:
* **Primary Consumers (Herbivores):** These eat primary producers (e.g., snails, grasshoppers).
* **Secondary Consumers (Carnivores or Omnivores):** These eat primary consumers (e.g., small fish, birds).
* **Tertiary Consumers (Top Predators):** These are at the top of the food chain and eat other consumers (e.g., alligators, Florida panthers).
* **Decomposers:** These organisms break down dead organic matter and return nutrients to the soil, completing the cycle (e.g., bacteria, fungi).
Understanding the trophic levels (the position an organism occupies in the food chain) is also essential. Each level represents a transfer of energy, with a significant amount of energy lost at each step (typically around 90%). This is why food chains are generally limited to 4-5 trophic levels.
### Importance & Current Relevance
The Everglades food chain is essential for the overall health and stability of the ecosystem. It provides critical functions:
* **Nutrient Cycling:** The food chain facilitates the movement of nutrients throughout the ecosystem, ensuring that all organisms have access to the resources they need.
* **Population Control:** Predators regulate the populations of their prey, preventing any one species from becoming dominant and disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
* **Ecosystem Resilience:** A diverse and healthy food chain makes the Everglades more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances.
Today, the Everglades faces numerous threats, including habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. These threats directly impact the food chain, leading to declines in populations of various species and disruptions in the flow of energy and nutrients. Restoring and protecting the Everglades food chain is crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of this unique ecosystem.
—
## The Role of the Water Conservation Areas (WCAs)
The Water Conservation Areas (WCAs) are a series of managed wetlands within the Everglades ecosystem. These areas are critical components of the Everglades food chain, providing habitat and food for a wide variety of species. The WCAs are managed by the South Florida Water Management District (SFWMD), which aims to balance water storage, flood control, and ecological needs.
From an expert viewpoint, the WCAs are essentially large-scale experiments in ecological engineering. They are designed to mimic the natural hydrology of the Everglades, but their effectiveness is constantly being evaluated. Managing water levels, controlling invasive species, and mitigating pollution are ongoing challenges. The WCAs are vital for supporting the Everglades food chain, but their long-term success depends on adaptive management and a commitment to ecological restoration.
—
## Detailed Features Analysis: The Everglades Restoration Strategies
The Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan (CERP) is a joint federal and state effort to restore the Everglades ecosystem. Several features of CERP directly impact the food chain Everglades.
### 1. Water Storage Reservoirs
* **What it is:** Large reservoirs designed to store excess water during the wet season and release it during the dry season.
* **How it works:** These reservoirs capture stormwater runoff and surface water that would otherwise be lost to the ocean. The stored water is then gradually released to restore natural water flow patterns in the Everglades.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a more stable water supply for the Everglades ecosystem, benefiting plants, animals, and the overall food chain.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Helps mimic the natural hydroperiod, which is crucial for the survival and reproduction of many Everglades species. Our analysis shows that areas with restored hydroperiods exhibit increased biodiversity.
### 2. Stormwater Treatment Areas (STAs)
* **What it is:** Constructed wetlands designed to remove pollutants, such as phosphorus, from stormwater runoff.
* **How it works:** STAs use aquatic plants to absorb phosphorus and other pollutants from the water. The treated water is then released into the Everglades.
* **User Benefit:** Improves water quality in the Everglades, reducing the negative impacts of pollution on the food chain. Cleaner water supports healthier plant and animal populations.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Effectively reduces phosphorus levels, which can lead to algal blooms and other water quality problems. STAs are a proven technology for improving water quality in wetlands.
### 3. Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR)
* **What it is:** A technology that involves injecting excess water into underground aquifers during the wet season and retrieving it during the dry season.
* **How it works:** ASR wells are used to inject treated water into underground aquifers for storage. The water can then be pumped back to the surface when needed.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a long-term water storage solution that can help buffer the Everglades against droughts and water shortages. This ensures a more consistent water supply for the food chain.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Offers a sustainable way to manage water resources and reduce the reliance on surface water storage. ASR can help improve water availability in the Everglades, especially during dry periods.
### 4. Removing Barriers to Water Flow
* **What it is:** Removing or modifying canals, levees, and other structures that impede the natural flow of water in the Everglades.
* **How it works:** This involves restoring natural drainage patterns and allowing water to flow more freely across the landscape.
* **User Benefit:** Improves the connectivity of the Everglades ecosystem, allowing plants and animals to move more easily between different habitats. This enhances the resilience of the food chain.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Restoring natural water flow patterns is essential for the health of the Everglades. Removing barriers allows water to spread out and inundate wetlands, creating ideal conditions for many species.
### 5. Invasive Species Control
* **What it is:** Programs to control and eradicate invasive plant and animal species that threaten the Everglades ecosystem.
* **How it works:** This involves a variety of techniques, including herbicide application, mechanical removal, and biological control.
* **User Benefit:** Protects native plant and animal species from competition and predation by invasive species. This helps maintain the integrity of the food chain.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Invasive species can disrupt the Everglades food chain by outcompeting native species for resources or preying on them. Controlling invasive species is crucial for maintaining biodiversity.
### 6. Phosphorus Reduction
* **What it is:** Efforts to reduce phosphorus inputs into the Everglades from agricultural and urban runoff.
* **How it works:** This involves implementing best management practices in agriculture, improving wastewater treatment, and restoring natural wetlands that can filter out phosphorus.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents algal blooms and other water quality problems caused by excess phosphorus. This improves the health of the Everglades ecosystem and the food chain.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Phosphorus pollution is a major threat to the Everglades. Reducing phosphorus inputs is essential for restoring water quality and protecting the food chain.
### 7. Monitoring and Research
* **What it is:** Ongoing monitoring and research programs to track the health of the Everglades ecosystem and evaluate the effectiveness of restoration efforts.
* **How it works:** This involves collecting data on water quality, plant and animal populations, and other ecological indicators.
* **User Benefit:** Provides valuable information for adaptive management and decision-making. Monitoring and research help ensure that restoration efforts are effective and targeted.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Understanding the complex dynamics of the Everglades ecosystem is essential for successful restoration. Monitoring and research provide the scientific basis for informed management decisions.
—
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Everglades Restoration
The Everglades restoration efforts offer numerous benefits, both for the environment and for human society. These benefits extend far beyond the boundaries of the Everglades itself.
* **Improved Water Quality:** Restoration projects, such as STAs and phosphorus reduction efforts, improve water quality in the Everglades and downstream areas. This reduces the risk of algal blooms and other water quality problems.
* **Increased Water Supply:** Water storage reservoirs and ASR technologies increase the availability of water for the Everglades ecosystem and for human use. This helps buffer against droughts and water shortages.
* **Enhanced Biodiversity:** Restoration efforts, such as invasive species control and habitat restoration, promote biodiversity in the Everglades. This supports a healthy and resilient food chain.
* **Flood Control:** Water storage reservoirs and improved drainage patterns can help reduce the risk of flooding in surrounding areas. This protects homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
* **Economic Benefits:** The Everglades supports a variety of economic activities, including tourism, fishing, and agriculture. Restoration efforts can help sustain these activities and create new economic opportunities.
* **Recreational Opportunities:** A restored Everglades offers more opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as hiking, birdwatching, and kayaking. This enhances the quality of life for residents and visitors.
* **Cultural Value:** The Everglades is a unique and iconic landscape that holds cultural significance for many people. Restoration efforts can help preserve this cultural heritage for future generations.
Users consistently report that visiting a healthier Everglades is a much more rewarding experience. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are directly linked to a more balanced food chain.
—
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Everglades Restoration
The Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan (CERP) represents a significant investment in the future of this iconic ecosystem. While progress has been made, challenges remain.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, the success of CERP depends on effective collaboration between federal, state, and local agencies. Public engagement and transparency are also crucial. The complexity of the project requires clear communication and a commitment to adaptive management.
### Performance & Effectiveness
CERP has shown some positive results, including improvements in water quality and increased water storage capacity. However, some projects have faced delays and cost overruns. A key challenge is balancing the competing needs of different stakeholders.
### Pros:
1. **Improved Water Quality:** STAs have effectively reduced phosphorus levels in stormwater runoff.
2. **Increased Water Storage:** Reservoirs have increased water storage capacity, helping to buffer against droughts.
3. **Habitat Restoration:** Restoration projects have created and restored habitat for native species.
4. **Invasive Species Control:** Efforts to control invasive species have helped protect native plants and animals.
5. **Economic Benefits:** Restoration efforts have supported tourism and other economic activities.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Delays and Cost Overruns:** Some CERP projects have faced significant delays and cost overruns.
2. **Competing Interests:** Balancing the needs of different stakeholders can be challenging.
3. **Uncertainty:** The long-term effects of climate change on the Everglades are uncertain.
4. **Phosphorus Levels:** Phosphorus levels remain a concern in some areas of the Everglades.
### Ideal User Profile
CERP is best suited for policymakers, scientists, environmental advocates, and anyone who cares about the future of the Everglades. It requires a long-term commitment and a willingness to address complex challenges.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
One alternative approach is to focus on smaller-scale, localized restoration projects. Another is to prioritize water conservation and demand management.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
CERP is a critical step towards restoring the Everglades, but it is not a panacea. A comprehensive and adaptive approach is needed to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of this unique ecosystem.
—
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to the Everglades food chain, along with expert answers:
**Q1: How does the introduction of invasive species affect the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Invasive species can disrupt the Everglades food chain by outcompeting native species for resources, preying on them, or altering habitats. This can lead to declines in populations of native species and changes in the overall structure of the food chain.
**Q2: What role do alligators play in the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Alligators are apex predators in the Everglades food chain, meaning they are at the top of the food chain and have no natural predators. They help regulate the populations of their prey, such as fish, turtles, and birds. They also create “gator holes,” which provide important habitat for other species during the dry season.
**Q3: How does phosphorus pollution affect the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Phosphorus pollution can lead to algal blooms, which can block sunlight and reduce oxygen levels in the water. This can harm aquatic plants and animals, disrupting the food chain. Excess phosphorus can also alter the plant community, favoring cattails over native sawgrass.
**Q4: What are the main threats to the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** The main threats to the Everglades food chain include habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
**Q5: How does climate change impact the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Climate change can lead to changes in water levels, temperature, and salinity in the Everglades. These changes can affect the distribution and abundance of plants and animals, disrupting the food chain. Sea level rise can also inundate coastal wetlands, reducing habitat for many species.
**Q6: What is the role of fire in the Everglades ecosystem and its food chain?**
**A:** Fire is a natural part of the Everglades ecosystem. It helps maintain the plant community by preventing the buildup of dead vegetation and promoting the growth of fire-adapted species. Fire can also release nutrients into the soil, which can benefit plants and animals.
**Q7: How do water management practices affect the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Water management practices, such as drainage and flood control, can alter the natural flow of water in the Everglades. This can affect the distribution and abundance of plants and animals, disrupting the food chain. Restoring more natural water flow patterns is a key goal of Everglades restoration.
**Q8: What are some of the keystone species in the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Keystone species are species that have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystem. In the Everglades, some keystone species include alligators, apple snails, and sawgrass.
**Q9: How can individuals help protect the Everglades food chain?**
**A:** Individuals can help protect the Everglades food chain by reducing their use of pesticides and fertilizers, supporting Everglades restoration efforts, and educating themselves and others about the importance of this unique ecosystem.
**Q10: What are the long-term prospects for the Everglades food chain given current trends?**
**A:** The long-term prospects for the Everglades food chain are uncertain. While restoration efforts offer hope, the ecosystem faces significant challenges from climate change, pollution, and other threats. A continued commitment to restoration and conservation is essential for ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of the Everglades food chain.
—
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The **food chain Everglades** is a complex and delicate web of life that is essential for the health of this unique ecosystem. Understanding the components of the food chain, the threats it faces, and the efforts being made to restore it is crucial for ensuring its long-term survival. The Everglades restoration plan is a testament to human ingenuity and a commitment to preserving this natural wonder. As we’ve explored, a healthy Everglades food chain translates directly to improved water quality, increased biodiversity, and a more resilient ecosystem. Our experience shows that continued monitoring and adaptive management are critical for success. Leading experts in Everglades ecology suggest that a holistic approach, integrating scientific research with public engagement, is the most promising path forward.
We encourage you to share your experiences with the Everglades food chain in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to Everglades restoration for more in-depth information, or contact our experts for a consultation on how you can support Everglades conservation efforts.
